VBA Len Function
Excel VBA Len function returns the number of characters in a string (length), including blank spaces, or bytes to store the variable type.
Syntax:
Len(Expression)
The VBA Len function accepts one argument, as described below.
Argument:
| Expression | - string, string variable or variant |
Notes about usage:
- If Expression is a zero-length string (""), then a value of zero (0) is returned.
- If a non-string variable is entered, then the bytes used to store that variable type is returned.
- In most cases, a Variant variable is treated as a string and the number of characters is returned. One exception is when a variant variable has all zeroes to the right of a decimal point. In this case, the number is treated as a whole (integer) number.
- Len returns the number of characters as a Long Integer value when measuring the length of a string or variant.
- Len returns the bytes to store a variable as an Integer value when the argument is any valid VBA data type other than string or variant.
- If the expression is the string itself, rather than a variable, then it must be set off by double quotes.
How to use Excel VBA Len function with string expressions
Dim str1 as string
str1 = "Annabelle is asleep."
Msgbox Len("Annabelle is asleep")
MsgBox Len(str1)
' Both return 20
Len accepts as an argument either a variable name in which is stored a string expression or the string itself, set off by double quotes. If the expression is a string, then the number of characters are returned. This count includes any blank spaces.
How to use Excel VBA Len function with variant expressions
Dim X as Variant
X = 1234#
MsgBox Len(X)
Returns
The Len function also accepts a variant variable as an argument. In most cases, the value is converted to a string as is and the number of characters is returned. One exception is when the variable is set equal to a numeric value with a decimal point having all zeros to the right of the decimal point.
In this example, X is first set equal to 1234.00, which is then stored as 1234#. Here, Len only counts characters up to the #, but does not count #, and returns a value of four (4). Next, X is set equal to 1234.01. This number is converted to a string retaining the decimal point and all integers to the right. Len returns a value of seven (7).
How to apply an Excel VBA Len function to an Excel spreadsheet
Dim str1 as String
str1 = Len(Cells(1, 1)
MsgBox str1
str1 = Len(Range("A1"))
MsgBox str1
Cells(1,2) = Len(Cells(1,1))
VBA Len can also interact with an Excel spreadsheet. In this example, the length of the value in the spreadsheet cell at A1 is recorded in the cell next to it, Cells(1, 2). We can access the contents of cells using with either the R1C1 notation or the A1 notation. See Interact with an Excel Spreadsheet.
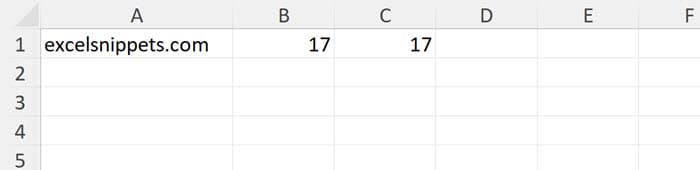
Here the R1C1 notation was used to store the value in the cell to the immediate right of "excelsnippets.com," while the A1 notation stores that same value in the cell next to it on the right.
Using Excel VBA Len with non-string data types
Dim I As Integer
Dim J As Long
Dim X1 As Boolean
Dim Y1 As Single
Dim Z1 As Double
MsgBox Len(I)
' Returns 2
MsgBox Len(J)
' Returns 4
MsgBox Len(X1)
' Returns 2
MsgBox Len(Y1)
' Returns 4
MsgBox Len(Z1)
' Returns 8
Originally Excel VBA LenB was the function used to measure the bytes required to store a variable, and it is still available. But Len will also return the bytes for non-string variables.
How to use Excel VBA LenB function
Dim str1 as string
str1="excelsnippets.com"
MsgBox Len(str1)
' Returns 17
MsgBox LenB(str1)
' Returns 34
The difference between Len and LenB is that Len returns the length of a string or variant, while LenB returns the bytes required to store a string or variant. For all other data types, they behave the same. The length of "excelsnippets.com" is seventeen (17) characters.
Note: Neither Len or LenB can accept Object or Array data types. Using either of these two data types will generate an error message and program execution will stop. They can, however, accept the elements of an array (individually). For example, Len(arr) will return an error message for arr() dimensioned as a variant array, but will return a value for arr(1) or any other element of the array.
